
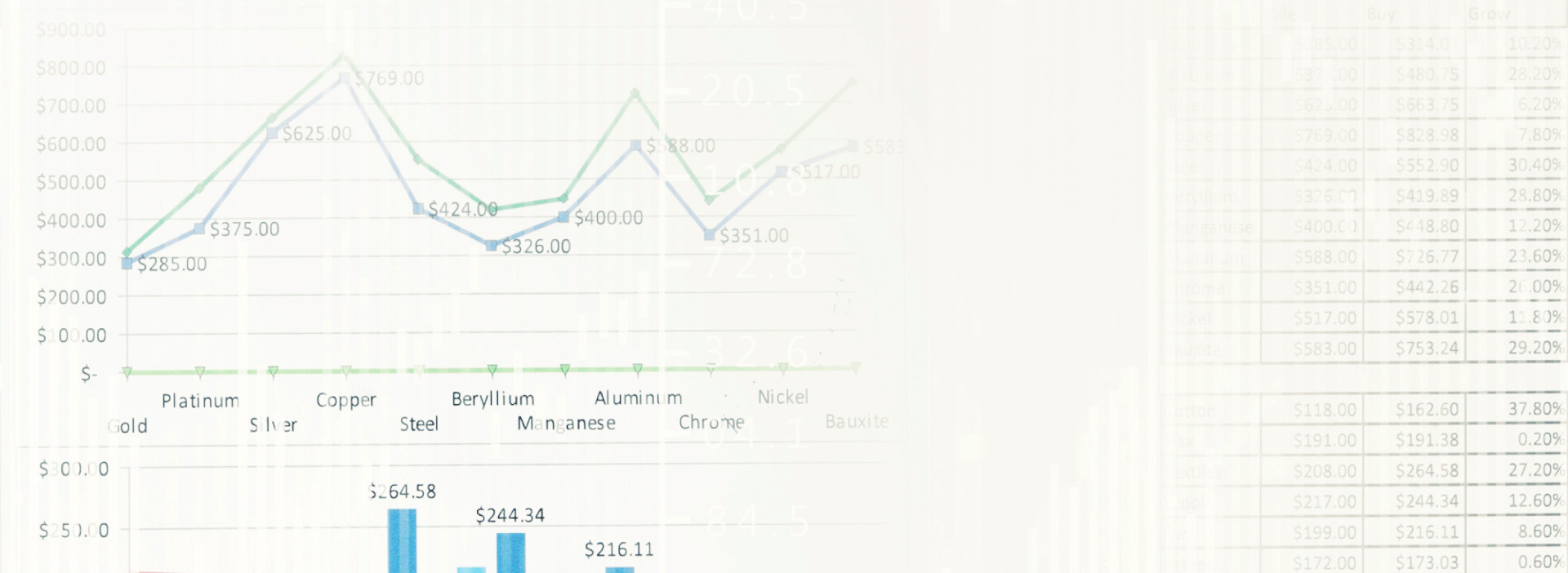
Charts, graphs, maps, and other visual formats bring data to life in a way that can be quickly and easily understood. The ability to visualize data and see it in context is one area where BI really shines. Managers and employees can use interactive features to customize which information they want to view, drill into data for further analysis, and share results with other stakeholders. They use continually updated charts, graphs, tables, and other types of data visualization to track pre-defined KPIs and other business metrics – and provide an at-a-glance overview of performance in near-real time. With modern querying tools, submitting a query can be as simple as asking Google (or even Siri) a question – like “Where are shipping delays happening?”, “Did quarterly sales meet their targets?”, or “How many widgets were sold yesterday?”ĭashboards are one of the most popular BI tools. Querying tools allow users to ask business questions and get answers through intuitive interfaces. Reports can be automated and sent out on a regular, predetermined schedule – or ad hoc and generated on the fly. They are also interactive, so users can slice and dice tables or drill deeper into data as needed. Reports use summaries and visual elements like charts and graphs to show users’ trends over time, relationships between variables, and much more. Here are some of the most common:īI reporting – presenting data and insights to end users in a way that is easy to understand and act on – is fundamental to every business. There are many different tools used in a business intelligence system.
USER PUBLISHING BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE DEFINITION SOFTWARE
Make data and reporting accessible to everyone. BI software offers intuitive interfaces, drag-and-drop reports, and role-based dashboards that team members can use themselves – without the need for coding or other technical skills.They can also identify areas of overlap, duplication, or inefficiencies across departments or subsidiaries in order to streamline operations. Operate more efficiently. Business intelligence systems allow everyone to spend less time hunting down information, analyzing data, and generating reports.Spot issues so they can be resolved. With BI, users can detect potential business problems before they cause financial harm – such as manufacturing or distribution bottlenecks, upward trends in customer churn, rising labor costs, and more.Identify and set benchmarks. BI solutions let organizations compare their processes and performance metrics to industry standards, determine where improvements are needed, set meaningful benchmarks, and monitor progress toward goals.
Measure and track performance. BI dashboards make it easy to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), track progress against targets, and set alerts to know where and when to focus improvement initiatives.

They can also assess their own capabilities, strengths, and weaknesses compared to competitors and use that information to their advantage. Gain and maintain competitive advantage. With timely BI, organizations can quickly identify and act on new trends and opportunities.Receive support for fact-based decision-making. BI tools help executives, managers, and workers uncover insights that are relevant to their roles and areas of responsibility – and use them to make decisions based on fact, not guesswork.Here are just a few of the many benefits of BI: A successful BI program shines light on ways to increase profits and performance, discover issues, optimize operations, and much more.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
